Nutrients Deficiency Symptoms in Jasmine Plant

Nutrients play a vital role in the growth, development, and overall health of jasmine plants whether grown indoor or outdoor. Just like any other flowering plants, jasmine plants need a balanced intake of essential nutrients to thrive and produce lush foliage, vibrant blooms, and healthy root systems.
These nutrients play crucial role for various physiological processes, including photosynthesis, enzyme activation, and cell structure formation. Insufficient or imbalanced nutrient levels can lead to deficiencies and thus affect the plant’s vigor and flower blooming.
Understanding the importance of nutrients in jasmine cultivation is crucial for maintaining optimal plant health and maximizing their ornamental value in gardens, landscapes, and indoor settings.
In this post, I will let you know the classification of nutrients and will describe nutrients deficiency symptoms in jasmine plant which will help you to take preventive and curative measures.
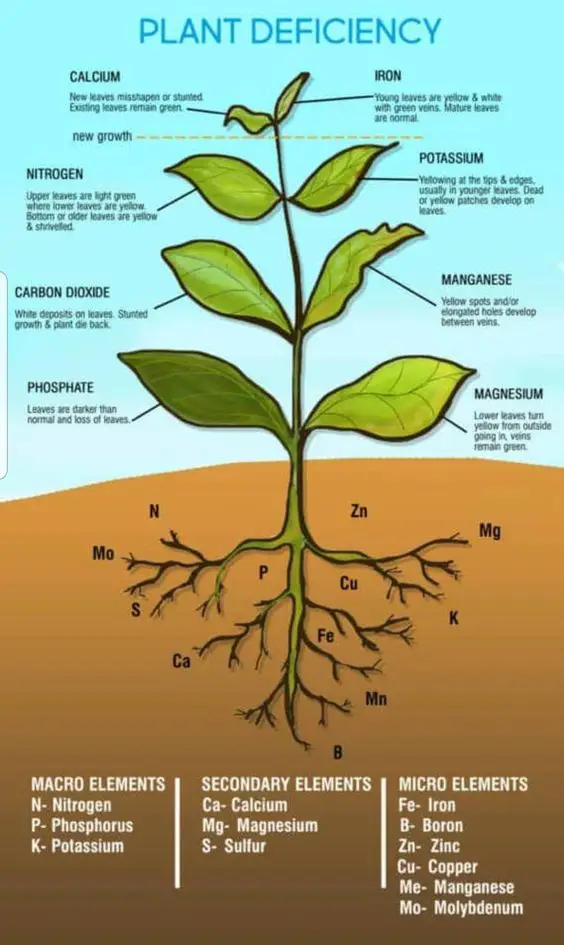
Classification of Nutrients
- Macro Nutrients
- secondary Nutrients
- Micro Nutrients
Macro Nutrients
Macronutrients are divided into three main elements.
Nitrogen
Promotes overall growth and vegetative growth. On deficiency, leaves turn yellow. Add organic compost or nitrogenous fertilizer.
Phosphorous
Aids in vegetative growth. Promote seed and flower formation. on deficiency, leaves are dark green with purple or brown spots. Stunted growth and absent or less flowering. Chicken, horse manure, bone meal, fish emulsion, and rock phosphate are rich sources of phosphorous. You can also add synthetic phosphatic fertilizer.
Potassium
Potassium is the third most important macro element which plays an important role in plant growth and development by regulating water uptake, improving disease resistance, enhancing photosynthesis, and promoting overall plant vigor. On deficiency, symptoms may include Marginal leaf scorching or browning, weak stems, reduced flower size and quality.
Add wood ash or potassium sulfate.
Wood ash is a good source of Potassium. It contains 5-7% Potassium and about 2% phosphorous and other elements in traces. The major component in wood ash is calcium (30-50%).
Secondary Elements
Secondary elements are also divided into three important elements.
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Sulfur
Calcium
It is important for plant cell wall structure and cell division. It aids in disease resistance and helps against environmental stresses.
Add gypsum or calcium-rich fertilizers to treat deficiency.
Magnesium
Magnesium plays an important role in energy transfer within the plant, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of proteins. Magnesium also helps regulate nutrient uptake and supports plant growth and development.
On deficiency, lower leaves turn yellow, while veins are green and stunted growth.
Apply magnesium sulfate (Epsom salt) or foliar sprays of magnesium.
Sulfur
Sulgur plays role in chlorophyll production. It influences the flavor and aroma and helps to tolerate environmental stresses such as drought and cold.
This deficiency leads to chlorosis. Plants become pale green or yellow. flowering is also reduced.
Add Organic matter or synthetic fertilizers like ammonium sulphate, magnesium sulphate or potassium sulphate.
Micro Nutrients
Micro Nutrients are divided into six (06) elements.
- Iron
- Zinc
- Boron
- Copper
- Manganese
- Molybdenum
Iron
It plays a role in enzyme activation and electron transport within cells. It helps in fighting against bacterial and fungal diseases.
on deficiency, yellowing of young leaves can be seen and there comes poor flowering if not treated in time.
Zinc
Zinc is an important regulatory component of various enzymes and proteins. In case of zinc deficiency in jasmine plants, leaf size is reduced, discoloration of leaves and reduced flowering.
Add Zinc sulfate or zinc chelates. You can also apply zinc foliar spray.
Boron
It regulates hormone levels and promotes health. It aids flower production and retention. Deficiency symptoms are crinkling of leaves, chlorosis, downward curling of leaf tips, absent flowering and poor root growth.
Apply Boron based fertilizer to treat boron deficiency.
Copper
Copper is also essential micro nutrient and play role in photosynthesis and and other metabolic processes. if plants are deficient, leaf tips are twisted and die back. in severe cases, plants die.
Copper-based fungicides, such as copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture, can be applied to jasmine plants to prevent or control fungal and bacterial diseases like powdery mildew, leaf spot, and bacterial blight.
Copper (Cu) toxicity in roots may arise when the total copper content exceeds 50 ppm in sandy soils and up to 150 ppm in silty-clay or clay soils.
Manganese
Manganese holds an importance for the development and elongation of the roots. It strengthens the roots for better absobtion of nutrients from the soil.
Manganese deficiency lead to chlorosis, poor root development, and reduced growth. in severe conditions, brown spots appear between veins and leaf magins become crinkled and wavy.
Add compost or organic matter. Use Manganese sulfate or manganese in chelated forms.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum play an important role in transferring nitrogen to amino acids.The deficiency symptoms resemble with nitrogen deficiency. Leaves turn yellow.
Apply ammonium molybdate or sodium molybdate.
I hope this information helped you!

I am Yasir Riaz, an Agronomist for more than a decade. Helping local farmers and Gardeners to improve their crops and Gardens and overall productivity. In addition to my work in agriculture, I have also delved into the digital world as an SEO writer and blogger. Through my blog, I aim to educate and inspire others about the Chameli Flower (Jasmine).






